Classroom Learning Activities
|
1. Food Security - What is this?
Food security means that everyone in the community has enough good, healthy, safe and culturally appropriate food to eat every day. For a nation, this means:
When identifying what is meant by food security, view the movies to the right and have the children answer the following questions:
Please Note: The World Food Programme has several of these short movies on their website and on Youtube. However, it is advisable that you preview them as some have disturbing images of malnourished children. |
How food secure are these people?
|
2. Food Travel Log - How far does your food travel?
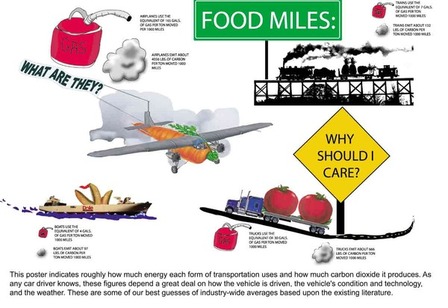
It is estimated that the average American meal travels about 1500 miles to get from farm to plate. Why is this cause for concern? There are many reasons:
It is estimated that the average American meal travels about 1500 miles to get from farm to plate. Why is this cause for concern? There are many reasons:
- This long-distance, large-scale transportation of food consumes large quantities of fossil fuels. It is estimated that we currently put almost 10 kcal of fossil fuel energy into our food system for every 1 kcal of energy we get as food.
- Transporting food over long distances also generates great quantities of carbon dioxide emissions. Some forms of transport are more polluting than others. Airfreight generates 50 times more CO2 than sea shipping. But sea shipping is slow, and in our increasing demand for fresh food, food is increasingly being shipped by faster - and more polluting -- means.
- In order to transport food long distances, much of it is picked while still unripe and then gassed to "ripen" it after transport, or it is highly processed in factories using preservatives, irradiation, and other means to keep it stable for transport and sale. Scientists are experimenting with genetic modification to produce longer-lasting, less perishable produce.
|
A really fun activity to do with children is the Food Travel Log.
A great resource for this activity is: How Far Did It Travel? |
Retrieved from 500 ECO
|
Relevant Convention Articles
Article 6
1. States Parties recognize that every child has the inherent right to life.
2. States Parties shall ensure to the maximum extent possible the survival and development of the child.
Article 24
1. States Parties recognize the right of the child to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of health and to facilities for the treatment of illness and rehabilitation of health. States Parties shall strive to ensure that no child is deprived of his or her right of access to such health care services.
2. States Parties shall pursue full implementation of this right and, in particular, shall take appropriate measures:
(a) To diminish infant and child mortality;
(b) To ensure the provision of necessary medical assistance and health care to all children with emphasis on the development of primary health care;
(c) To combat disease and malnutrition, including within the framework of primary health care, through, inter alia, the application of readily available technology and through the provision of adequate nutritious foods and clean drinking-water, taking into consideration the dangers and risks of environmental pollution;
(d) To ensure appropriate pre-natal and post-natal health care for mothers;
(e) To ensure that all segments of society, in particular parents and children, are informed, have access to education and are supported in the use of basic knowledge of child health and nutrition, the advantages of breastfeeding, hygiene and environmental sanitation and the prevention of accidents;
(f) To develop preventive health care, guidance for parents and family planning education and services.
3. States Parties shall take all effective and appropriate measures with a view to abolishing traditional practices prejudicial to the health of children.
4. States Parties undertake to promote and encourage international co-operation with a view to achieving progressively the full realization of the right recognized in the present article. In this regard, particular account shall be taken of the needs of developing countries.
1. States Parties recognize that every child has the inherent right to life.
2. States Parties shall ensure to the maximum extent possible the survival and development of the child.
Article 24
1. States Parties recognize the right of the child to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of health and to facilities for the treatment of illness and rehabilitation of health. States Parties shall strive to ensure that no child is deprived of his or her right of access to such health care services.
2. States Parties shall pursue full implementation of this right and, in particular, shall take appropriate measures:
(a) To diminish infant and child mortality;
(b) To ensure the provision of necessary medical assistance and health care to all children with emphasis on the development of primary health care;
(c) To combat disease and malnutrition, including within the framework of primary health care, through, inter alia, the application of readily available technology and through the provision of adequate nutritious foods and clean drinking-water, taking into consideration the dangers and risks of environmental pollution;
(d) To ensure appropriate pre-natal and post-natal health care for mothers;
(e) To ensure that all segments of society, in particular parents and children, are informed, have access to education and are supported in the use of basic knowledge of child health and nutrition, the advantages of breastfeeding, hygiene and environmental sanitation and the prevention of accidents;
(f) To develop preventive health care, guidance for parents and family planning education and services.
3. States Parties shall take all effective and appropriate measures with a view to abolishing traditional practices prejudicial to the health of children.
4. States Parties undertake to promote and encourage international co-operation with a view to achieving progressively the full realization of the right recognized in the present article. In this regard, particular account shall be taken of the needs of developing countries.
Online Resources and References
CitizenKid Central - Learn: Food Security
Cuesa - Cultivating a Healthy Food System
Food Hub - Food Miles
Take Part - Food, Inc.
Leopold Center Marketing - How far do does your food travel?
Oklahoma 4H - How Far did it Travel?
Plan - Planned Lifetime Advocacy Network
World Food Programme
Cuesa - Cultivating a Healthy Food System
Food Hub - Food Miles
Take Part - Food, Inc.
Leopold Center Marketing - How far do does your food travel?
Oklahoma 4H - How Far did it Travel?
Plan - Planned Lifetime Advocacy Network
World Food Programme